本系列文章转载自南峰子的技术博客
本文原地址:Objective-C Runtime 运行时之一:类与对象
Objective-C 语言是一门动态语言,它将很多静态语言在编译和链接时期做的事放到了运行时来处理。这种动态语言的优势在于:我们写代码时更具灵活性,如我们可以把消息转发给我们想要的对象,或者随意交换一个方法的实现等。
这种特性意味着 Objective-C 不仅需要一个编译器,还需要一个运行时系统来执行编译的代码。对于 Objective-C 来说,这个运行时系统就像一个操作系统一样:它让所有的工作可以正常的运行。这个运行时系统即 Objc Runtime。Objc Runtime 其实是一个 Runtime 库,它基本上是用 C 和汇编写的,这个库使得 C 语言有了面向对象的能力。
Runtime库主要做下面几件事:
- 封装:在这个库中,对象可以用 C 语言中的结构体表示,而方法可以用C函数来实现,另外再加上了一些额外的特性。这些结构体和函数被runtime函数封装后,我们就可以在程序运行时创建,检查,修改类、对象和它们的方法了。
- 找出方法的最终执行代码:当程序执行
[object doSomething]时,会向消息接收者(object)发送一条消息(doSomething),runtime 会根据消息接收者是否能响应该消息而做出不同的反应。这将在后面详细介绍。
Objective-C runtime 目前有两个版本: Modern runtime 和 Legacy runtime。 Modern Runtime 覆盖了64位的Mac OS X Apps,还有iOS Apps,Legacy Runtime 是早期用来给32位 Mac OS X Apps 用的,现在也就是可以不用管就是了。
在这一系列文章中,我们将介绍runtime的基本工作原理,以及如何利用它让我们的程序变得更加灵活。在本文中,我们先来介绍一下类与对象,这是面向对象的基础,我们看看在Runtime中,类是如何实现的。
类与对象基础数据结构
Class
Objective-C 类是由 Class 类型来表示的,它实际上是一个指向 objc_class结构体的指针。它的定义如下:
|
|
查看 objc/runtime.h 中 objc_class 结构体的定义如下:
|
|
在这个定义中,下面几个字段是我们感兴趣的:
isa:需要注意的是在 Objective-C 中,所有的类自身也是一个对象,这个对象的Class里面也有一个isa指针,它指向metaClass(元类),我们会在后面介绍它。super_class:指向该类的父类,如果该类已经是最顶层的根类(如NSObject或NSProxy),则super_class为NULL。cache:用于缓存最近使用的方法。一个接收者对象接收到一个消息时,它会根据isa指针去查找能够响应这个消息的对象。在实际使用中,这个对象只有一部分方法是常用的,很多方法其实很少用或者根本用不上。这种情况下,如果每次消息来时,我们都是methodLists中遍历一遍,性能势必很差。这时,cache就派上用场了。在我们每次调用过一个方法后,这个方法就会被缓存到cache列表中,下次调用的时候 runtime 就会优先去cache中查找,如果cache没有,才去methodLists中查找方法。这样,对于那些经常用到的方法的调用,但提高了调用的效率。version:我们可以使用这个字段来提供类的版本信息。这对于对象的序列化非常有用,它可是让我们识别出不同类定义版本中实例变量布局的改变
针对 cache,我们用下面例子来说明其执行过程:
|
|
objc_object 与 id
objc_object是表示一个类的实例的结构体,它的定义如下(objc/objc.h):
|
|
可以看到,这个结构体只有一个字体,即指向其类的 isa 指针。这样,当我们向一个 Objective-C 对象发送消息时,运行时库会根据实例对象的 isa 指针找到这个实例对象所属的类。Runtime 库会在类的方法列表及父类的方法列表中去寻找与消息对应的 selector 指向的方法。找到后即运行这个方法。
当创建一个特定类的实例对象时,分配的内存包含一个 objc_object 数据结构,然后是类的实例变量的数据。NSObject 类的 alloc 和 allocWithZone: 方法使用函数 class_createInstance 来创建 objc_object 数据结构。
另外还有我们常见的 id,它是一个objc_object 结构类型的指针。它的存在可以让我们实现类似于 C++ 中泛型的一些操作。该类型的对象可以转换为任何一种对象,有点类似于C语言中 void * 指针类型的作用。
objc_cache
上面提到了 objc_class 结构体中的 cache 字段,它用于缓存调用过的方法。这个字段是一个指向 objc_cache 结构体的指针,其定义如下:
|
|
该结构体的字段描述如下:
mask:一个整数,指定分配的缓存bucket的总数。在方法查找过程中,Objective-C runtime 使用这个字段来确定开始线性查找数组的索引位置。指向方法selector的指针与该字段做一个AND位操作(index = (mask & selector))。这可以作为一个简单的hash散列算法。occupied:一个整数,指定实际占用的缓存bucket的总数。buckets:指向Method数据结构指针的数组。这个数组可能包含不超过mask+1 个元素。需要注意的是,指针可能是NULL,表示这个缓存bucket没有被占用,另外被占用的bucket可能是不连续的。这个数组可能会随着时间而增长
元类(Meta Class)
在上面我们提到,所有的类自身也是一个对象,我们可以向这个对象发送消息(即调用类方法)。如:
|
|
这个例子中,+array 消息发送给了 NSArray 类,而这个 NSArray 也是一个对象。既然是对象,那么它也是一个objc_object 指针,它包含一个指向其类的一个 isa 指针。那么这些就有一个问题了,这个 isa 指针指向什么呢?为了调用 +array 方法,这个类的 isa指针必须指向一个包含这些类方法的一个objc_class 结构体。这就引出了meta-class的概念
meta-class是一个类对象的类
当我们向一个对象发送消息时,runtime 会在这个对象所属的这个类的方法列表中查找方法;而向一个类发送消息时,会在这个类的 meta-class 的方法列表中查找。
meta-class 之所以重要,是因为它存储着一个类的所有类方法。每个类都会有一个单独的 meta-class,因为每个类的类方法基本不可能完全相同。
再深入一下,meta-class 也是一个类,也可以向它发送一个消息,那么它的 isa 又是指向什么呢?为了不让这种结构无限延伸下去,Objective-C 的设计者让所有的 meta-class 的 isa 指向基类的meta-class,以此作为它们的所属类。即,任何 NSObject 继承体系下的 meta-class 都使用 NSObject 的 meta-class 作为自己的所属类,而基类的 meta-class 的 isa 指针是指向它自己。这样就形成了一个完美的闭环。
通过上面的描述,再加上对 objc_class 结构体中 super_class 指针的分析,我们就可以描绘出类及相应 meta-class 类的一个继承体系了,如下图所示:
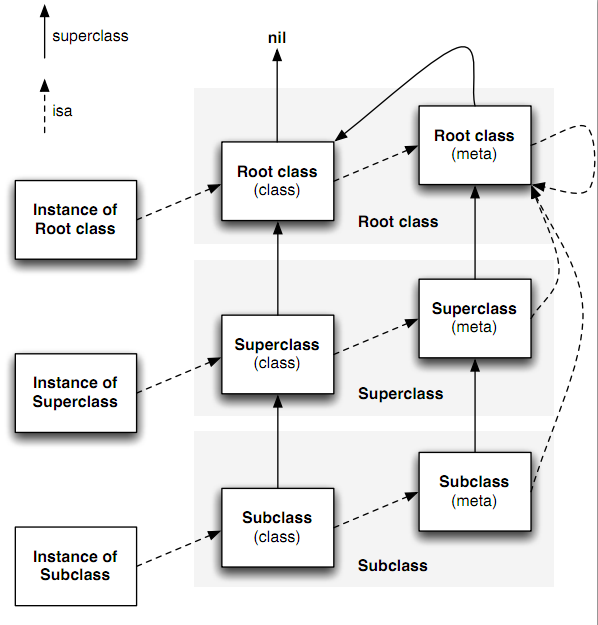
对于 NSObject 继承体系来说,其实例方法对体系中的所有实例、类和 meta-class 都是有效的;而类方法对于体系内的所有类和 meta-class 都是有效的。
讲了这么多,我们还是来写个例子吧:
|
|
这个例子是在运行时创建了一个 NSError 的子类 TestClass,然后为这个子类添加一个方法 testMetaClass,这个方法的实现是 TestMetaClass 函数。
运行后,打印结果是:
|
|
我们在 for 循环中,我们通过 objc_getClass 来获取对象的 isa,并将其打印出来,依此一直回溯到 NSObject 的 meta-class。分析打印结果,可以看到最后指针指向的地址是0x0,即 NSObject 的 meta-class 的类地址。
这里需要注意的是:我们在一个类对象调用 class 方法是无法获取
meta-class,它只是返回类而已
类与对象操作函数
runtime 提供了大量的函数来操作类与对象。类的操作方法大部分是以 class_ 为前缀的,而对象的操作方法大部分是以 objc_ 或 object_ 为前缀。下面我们将根据这些方法的用途来分类讨论这些方法的使用。
类相关操作函数
我们可以回过头去看看 objc_class 的定义,runtime 提供的操作类的方法主要就是针对这个结构体中的各个字段的。下面我们分别介绍这一些的函数。并在最后以实例来演示这些函数的具体用法
类名(name)
类名操作的函数主要有:
|
|
对于
class_getName函数,如果传入的cls为Nil,则返回一个字字符串
父类(super_class)和元类(meta-class)
父类和元类操作的函数主要有:
|
|
class_getSuperclass函数,当cls为Nil或者cls为根类时,返回Nil。不过通常我们可以使用NSObject类的superclass方法来达到同样的目的class_isMetaClass函数,如果是cls是元类,则返回 YES;如果否或者传入的cls为Nil,则返回NO
实例变量大小(instance_size)
实例变量大小操作的函数有:
|
|
成员变量(ivars)及属性
在 objc_class 中,所有的成员变量、属性的信息是放在链表 ivars 中的。ivars 是一个数组,数组中每个元素是指向 Ivar (变量信息)的指针。runtime提供了丰富的函数来操作这一字段。大体上可以分为以下几类:
1 成员变量操作函数,主要包含以下函数:
|
|
class_getInstanceVariable函数,它返回一个指向包含 name 指定的成员变量信息的objc_ivar结构体的指针(Ivar)class_getClassVariable函数,目前没有找到关于 Objective-C 中类变量的信息,一般认为 Objective-C 不支持类变量。注意,返回的列表不包含父类的成员变量和属性- Objective-C 不支持往已存在的类中添加实例变量,因此不管是系统库提供的提供的类,还是我们自定义的类,都无法动态添加成员变量。但如果我们通过运行时来创建一个类的话,又应该如何给它添加成员变量呢?这时我们就可以使用
class_addIvar函数了。不过需要注意的是,这个方法只能在objc_allocateClassPair函数与objc_registerClassPair之间调用。另外,这个类也不能是元类。成员变量的按字节最小对齐量是1<<alignment。这取决于ivar的类型和机器的架构。如果变量的类型是指针类型,则传递log2(sizeof(pointer_type))lass_copyIvarList函数,它返回一个指向成员变量信息的数组,数组中每个元素是指向该成员变量信息的objc_ivar结构体的指针。这个数组不包含在父类中声明的变量。outCount指针返回数组的大小。需要注意的是,我们必须使用free()来释放这个数组。
2 属性操作函数,主要包含以下函数:
|
|
这一种方法也是针对 ivars 来操作,不过只操作那些是属性的值。我们在后面介绍属性时会再遇到这些函数。
3 在 MAC OS X 系统中,我们可以使用垃圾回收器。runtime提供了几个函数来确定一个对象的内存区域是否可以被垃圾回收器扫描,以处理 strong/weak 引用。这几个函数定义如下:
|
|
但通常情况下,我们不需要去主动调用这些方法;在调用 objc_registerClassPair 时,会生成合理的布局。在此不详细介绍这些函数
方法(methodLists)
方法操作主要有以下函数:
|
|
class_addMethod的实现会覆盖父类的方法实现,但不会取代本类中已存在的实现,如果本类中包含一个同名的实现,则函数会返回NO。如果要修改已存在实现,可以使用method_setImplementation。一个Objective-C方法是一个简单的C函数,它至少包含两个参数self和_cmd。所以,我们的实现函数(IMP参数指向的函数)至少需要两个参数,如下所示:
|
|
与成员变量不同的是,我们可以为类动态添加方法,不管这个类是否已存在。
另外,参数 types 是一个描述传递给方法的参数类型的字符数组,这就涉及到类型编码,我们将在后面介绍
class_getInstanceMethod、class_getClassMethod函数,与class_copyMethodList不同的是,这两个函数都会去搜索父类的实现class_copyMethodList函数,返回包含所有实例方法的数组,如果需要获取类方法,则可以使用class_copyMethodList(object_getClass(cls), &count)(一个类的实例方法是定义在元类里面)。该列表不包含父类实现的方法。outCount参数返回方法的个数。在获取到列表后,我们需要使用free()方法来释放它class_replaceMethod函数,该函数的行为可以分为两种:如果类中不存在name指定的方法,则类似于class_addMethod函数一样会添加方法;如果类中已存在name指定的方法,则类似于method_setImplementation一样替代原方法的实现class_getMethodImplementation函数,该函数在向类实例发送消息时会被调用,并返回一个指向方法实现函数的指针。这个函数会比method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod(cls, name))更快。返回的函数指针可能是一个指向runtime 内部的函数,而不一定是方法的实际实现。例如,如果类实例无法响应selector,则返回的函数指针将是运行时消息转发机制的一部分class_respondsToSelector函数,我们通常使用NSObject类的respondsToSelector:或instancesRespondToSelector:方法来达到相同目的
协议(objc_protocol_list)
协议相关的操作包含以下函数:
|
|
class_conformsToProtocol函数可以使用NSObject类的conformsToProtocol:方法来替代class_copyProtocolList函数返回的是一个数组,在使用后我们需要使用free()手动释放
版本(version)
版本相关的操作包含以下函数:
|
|
其它
runtime 还提供了两个函数来供 CoreFoundation 的 tool-free bridging 使用,即:
|
|
通常我们不直接使用这两个函数
实例(Example)
上面列举了大量类操作的函数,下面我们写个实例,来看看这些函数的实例效果:
|
|
这段程序的输出如下:
|
|
动态创建类和对象
runtime 的强大之处在于它能在运行时创建类和对
动态创建类
动态创建类涉及到以下几个函数:
|
|
objc_allocateClassPair函数:如果我们要创建一个根类,则superclass指定为Nil。extraBytes通常指定为0,该参数是分配给类和元类对象尾部的索引ivars的字节数
为了创建一个新类,我们需要调用 objc_allocateClassPair,然后使用诸如 class_addMethod,class_addIvar 等函数来为新创建的类添加方法、实例变量和属性等。完成这些后,我们需要调用objc_registerClassPair 函数来注册类,之后这个新类就可以在程序中使用了
在前面介绍元类时,我们已经有接触到这几个函数了,在此我们再举个实例来看看这几个函数的使用:
|
|
程序的输出如下:
|
|
动态创建对象
动态创建对象的函数如下:
|
|
class_createInstance函数:创建实例时,会在默认的内存区域为类分配内存。extraBytes参数表示分配的额外字节数。这些额外的字节可用于存储在类定义中所定义的实例变量之外的实例变量。该函数在 ARC 环境下无法使用
调用 class_createInstance 的效果与 +alloc 方法类似。不过在使用 class_createInstance 时,我们需要确切的知道我们要用它来做什么。在下面的例子中,我们用 NSString 来测试一下该函数的实际效果:
|
|
输出结果是:
|
|
可以看到,使用 class_createInstance 函数获取的是 NSString 实例,而不是类簇中的默认占位符类 __NSCFConstantString
objc_constructInstance函数:在指定的位置(bytes)创建类实例objc_destructInstance函数:销毁一个类的实例,但不会释放并移除任何与其相关的引用
实例操作函数
实例操作函数主要是针对我们创建的实例对象的一系列操作函数,我们可以使用这组函数来从实例对象中获取我们想要的一些信息,如实例对象中变量的值。这组函数可以分为三小类:
- 针对整个对象进行操作的函数,这类函数包含
|
|
有这样一种场景,假设我们有类A和类B,且类B是类A的子类。类B通过添加一些额外的属性来扩展类A。现在我们创建了一个A类的实例对象,并希望在运行时将这个对象转换为B类的实例对象,这样可以添加数据到B类的属性中。这种情况下,我们没有办法直接转换,因为B类的实例会比A类的实例更大,没有足够的空间来放置对象。此时,我们就要以使用以上几个函数来处理这种情况,如下代码所示:
|
|
- 针对对象实例变量进行操作的函数,这类函数包含:
|
|
如果实例变量的 Ivar 已经知道,那么调用 object_getIvar 会比 object_getInstanceVariable 函数快,相同情况下,object_setIvar 也比 object_setInstanceVariable 快
3.针对对象的类进行操作的函数,这类函数包含:
|
|
获取类定义
Objective-C 动态运行库会自动注册我们代码中定义的所有的类。我们也可以在运行时创建类定义并使用 objc_addClass 函数来注册它们。runtime 提供了一系列函数来获取类定义相关的信息,这些函数主要包括:
|
|
objc_getClassList函数:获取已注册的类定义的列表。我们不能假设从该函数中获取的类对象是继承自NSObject体系的,所以在这些类上调用方法是,都应该先检测一下这个方法是否在这个类中实现
下面代码演示了该函数的用法:
|
|
输出结果如下:
|
|
- 获取类定义的方法有三个:
objc_lookUpClass,objc_getClass和objc_getRequiredClass。如果类在运行时未注册,则objc_lookUpClass会返回nil,而objc_getClass会调用类处理回调,并再次确认类是否注册,如果确认未注册,再返回nil。而objc_getRequiredClass函数的操作与objc_getClass相同,只不过如果没有找到类,则会杀死进程objc_getMetaClass函数:如果指定的类没有注册,则该函数会调用类处理回调,并再次确认类是否注册,如果确认未注册,再返回nil。不过,每个类定义都必须有一个有效的元类定义,所以这个函数总是会返回一个元类定义,不管它是否有效。
小结
在这一章中我们介绍了 Runtime 运行时中与类和对象相关的数据结构,通过这些数据函数,我们可以管窥 Objective-C 底层面向对象实现的一些信息。另外,通过丰富的操作函数,可以灵活地对这些数据进行操作
参考
- Objective-C Runtime Reference
- Objective-C Runtime的数据类型
- 详解Objective-C的meta-class
- what are class_setIvarLayout and class_getIvarLayout?
- What’s the difference between doing alloc and class_createInstance
本人刚开始写博客,主要是为了给自己的知识点做一个笔记,方便自己以后查阅,如果能让别人有所启发也是荣幸之至!如有错误,欢迎指正!